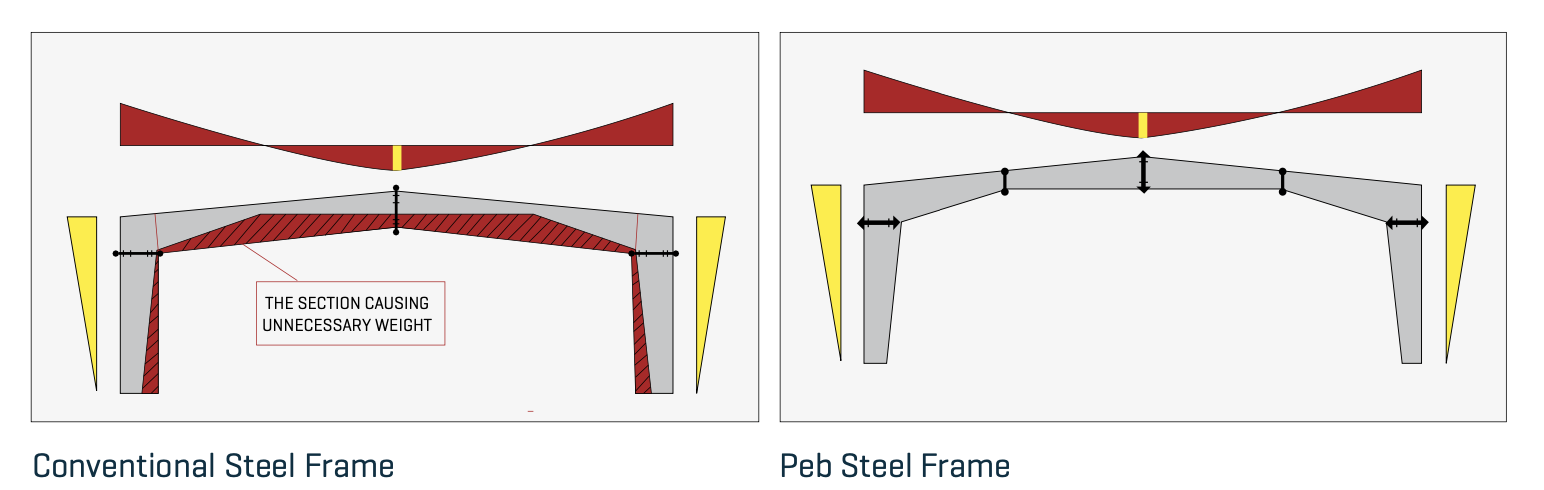
 Pre Engineering Buildings
Pre Engineering Buildings
A Pre-Engineering Building (PEB) is a structure that is designed and fabricated using a set of standardized techniques and components, typically in a factory setting. These buildings are known for their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and rapid construction. The use of PEBs has gained popularity in various industrial, commercial, and institutional sectors due to their numerous advantages.
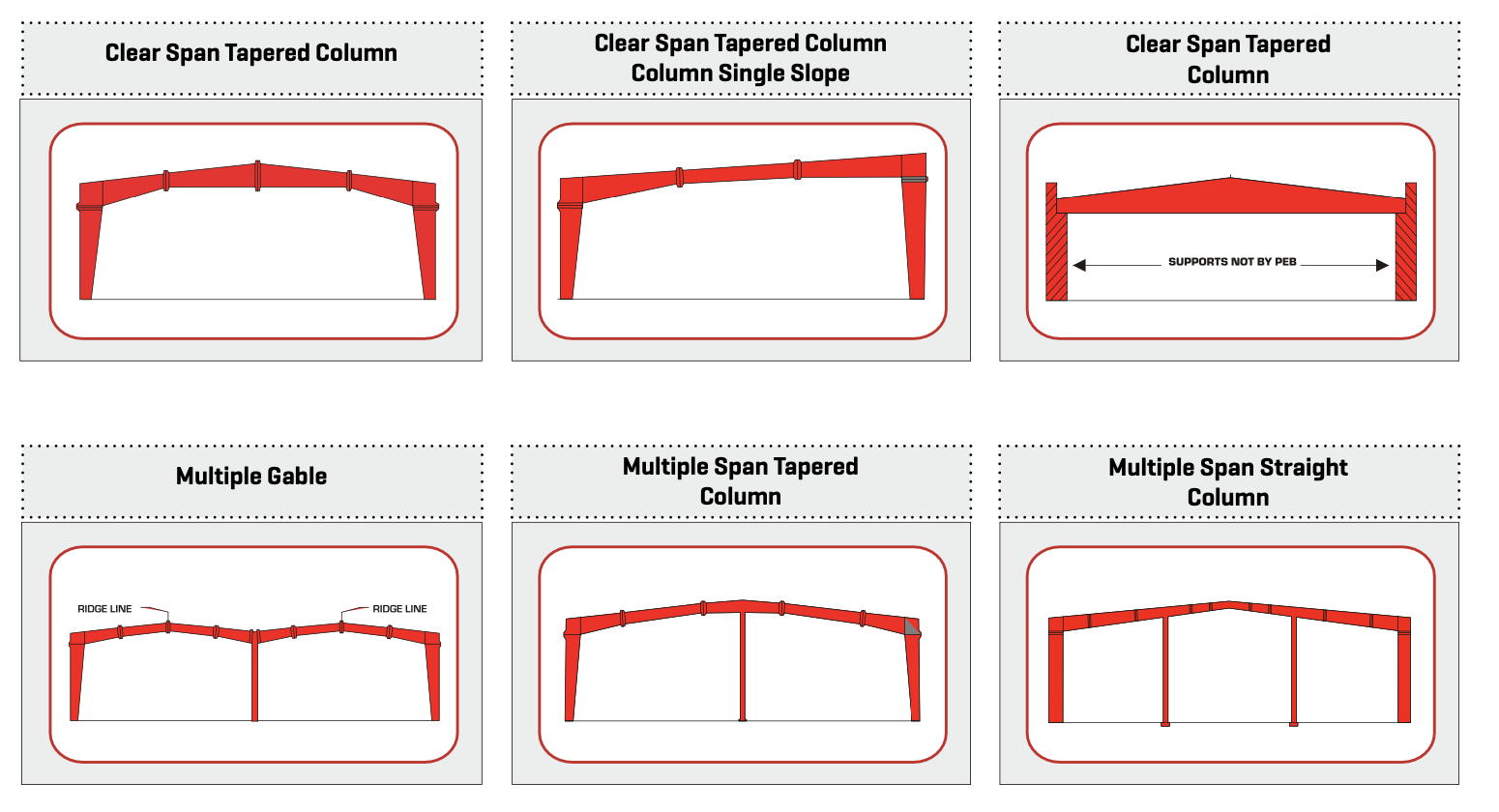
Key Components of a Pre-Engineering Building:
- Primary Framing:
- The main structural components, including rigid frames, are pre-designed and manufactured. These frames are made of steel and serve as the skeleton of the building.
- Secondary Framing:
- Components like purlins, girts, and eave struts form the secondary framing. They provide additional support and stability to the structure.
- Roof and Wall Panels:
- PEBs typically use insulated metal panels for roofing and wall cladding. These panels are lightweight, durable, and contribute to the energy efficiency of the building.
- Crane Systems:
- For industrial applications, PEBs often incorporate crane systems that are designed to meet specific load requirements. These systems are integrated during the fabrication process.
- Doors and Windows:
- Openings for doors and windows are pre-determined in the design phase, and the building components are fabricated to accommodate them.
Advantages of Pre-Engineering Buildings:
- Cost-Effective:
- PEBs are generally more cost-effective than traditional construction methods due to the efficiency of the manufacturing process and reduced on-site labor requirements.
- Speed of Construction:
- The majority of the building components are pre-fabricated, leading to faster construction times compared to conventional building methods.
- Design Flexibility:
- PEBs offer design flexibility, allowing for customization based on the specific needs and requirements of the client. This makes them suitable for a variety of applications.
- Energy Efficiency:
- The use of insulated metal panels contributes to energy efficiency, providing better insulation and reducing overall energy consumption.
- Quality Control:
- The manufacturing process in a controlled environment ensures a high level of quality control, resulting in consistent and reliable structures.
-
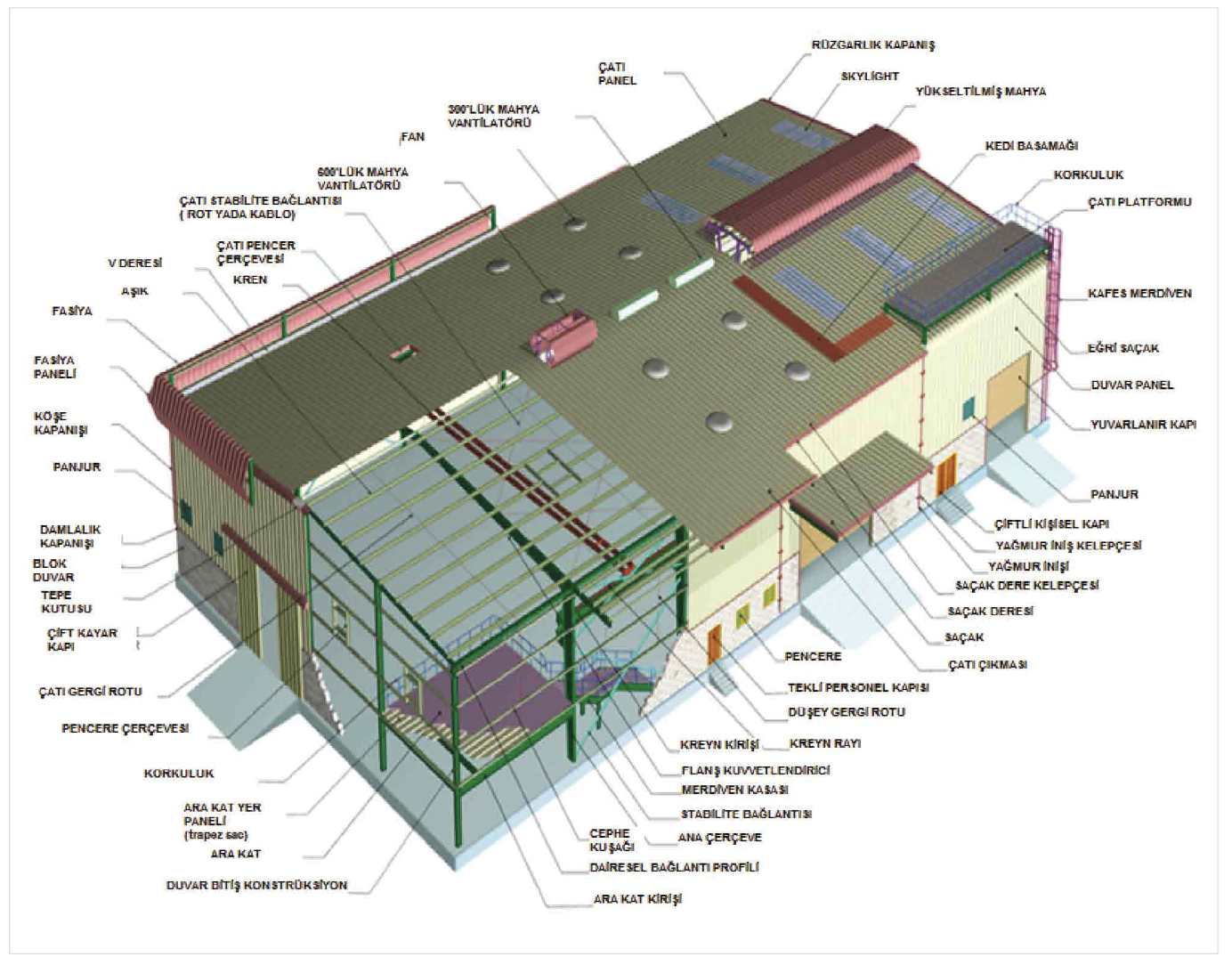 Applications of Pre-Engineering Buildings:
Applications of Pre-Engineering Buildings:
- Industrial Warehouses and Factories:
- PEBs are commonly used for constructing industrial facilities due to their quick construction and cost-effectiveness.
- Commercial Buildings:
- Offices, retail spaces, and other commercial structures can benefit from the speed and efficiency of PEB construction.
- Agricultural Buildings:
- PEBs are suitable for constructing barns, storage sheds, and other agricultural facilities.
- Institutional Buildings:
- Schools, hospitals, and other institutional structures can be efficiently constructed using pre-engineered building systems.
In conclusion, Pre-Engineering Buildings offer a modern and efficient approach to construction, making them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. Their cost-effectiveness, speed of construction, and adaptability to various designs contribute to their widespread use in the construction industry.
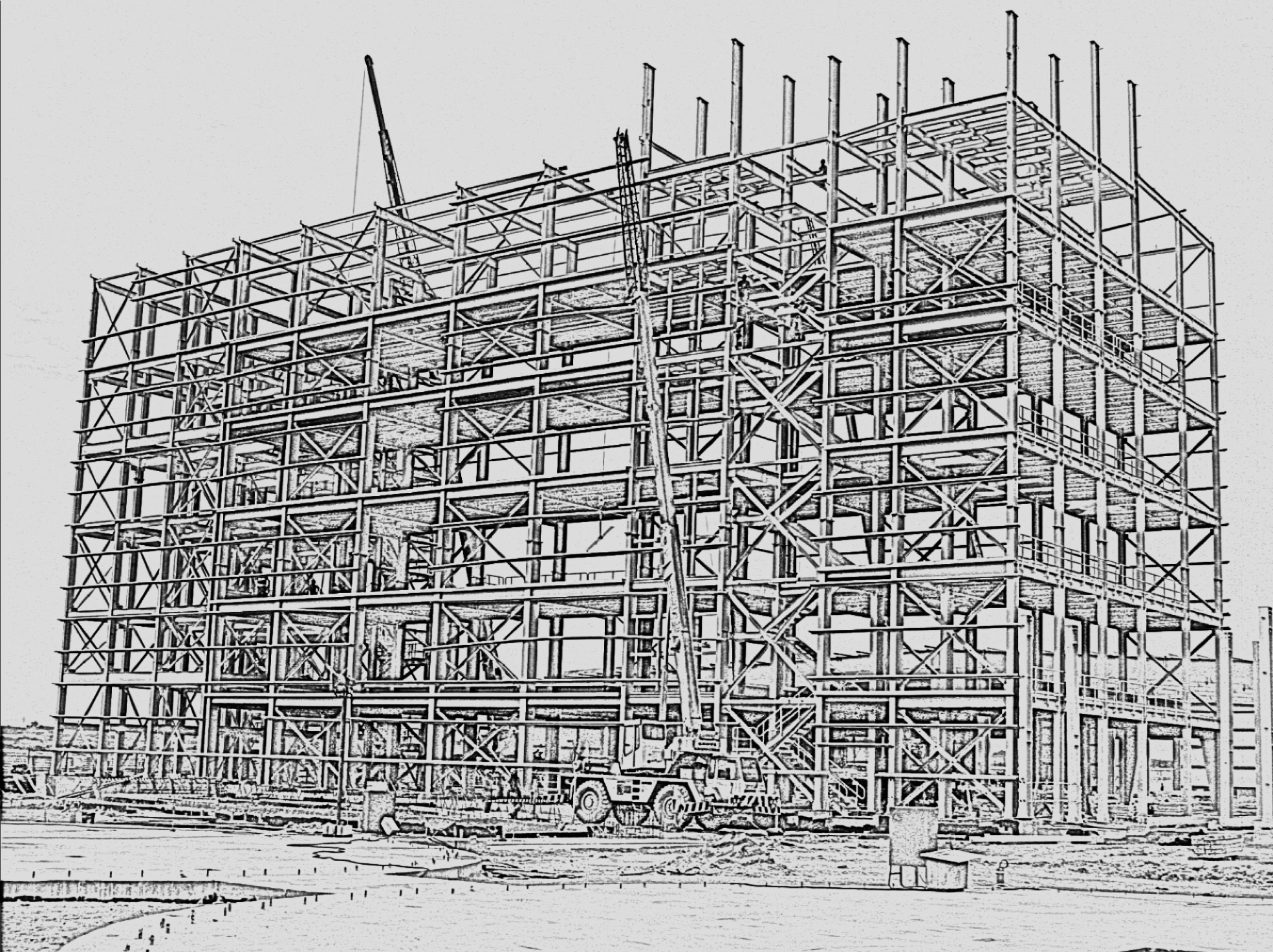
 Pre Engineering Buildings
Pre Engineering Buildings
 Applications of Pre-Engineering Buildings:
Applications of Pre-Engineering Buildings: